
Blue Ridge Physiography: Special Features (Part 1)
Special physiographic features of Virginia’s Piedmont and Blue Ridge include:
1. Aerial tour of the Southern Blue Ridge
Aerial Tour of the Southern Blue Ridge
• The Blue Ridge in southwestern Virginia is dramatically different from the northern Blue Ridge. The southern Blue Ridge is a broad, highland plateau that has even higher peaks, including Mount Rogers, reaching above the stream-eroded plateau surface.
• The following aerial tour takes an airplane trip across the southern Blue Ridge in Virginia. These views are typical of the beautiful scenery and interesting geology in this region.
Aerial Tour Location Map. (Maps courtesy of the Virginia Division of Geology and Mineral Resources)
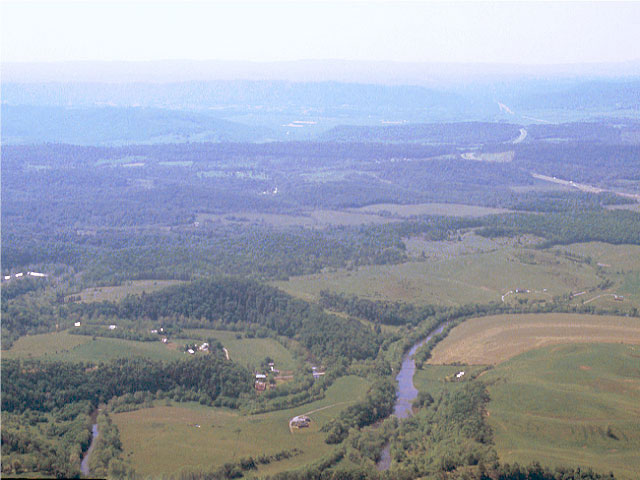

Looking east across the Valley and Ridge in southern Pulaski County to the foothills along the western edge of the Blue Ridge in the distance. These rocks in these foothills are Chilhowee Group sedimentary rocks, late Precambrian to early Paleozoic shales, conglomerates, and sandstones. (Photograph by Robert Whisonant)
<Back to Aerial Tour Location Map>
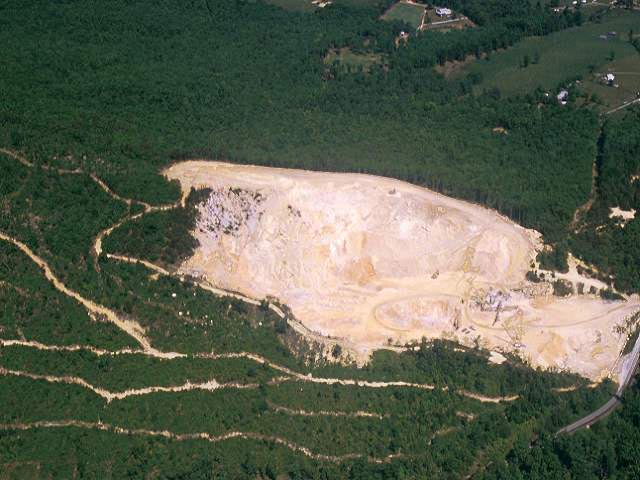

Quarry in Antietam Sandstone (Chilhowee Group) in the Blue Ridge south of Wytheville in Wythe County. The Antietam is a quartz-rich sandstone commonly found along the western flanks of the Blue Ridge. (Photograph by Robert Whisonant)
<Back to Aerial Tour Location Map>